As we begin to crest into the era of automobile electrification, it has become increasingly difficult to recall all of the outstanding hybrid technologies we already have on tap. With all the noise being made (or lack thereof when it comes to the engine sounds) amidst this monumental shift, it would be completely unfair to acknowledge hybrid engines as being merely a stopgap solution while we wait for electric EVs to take over as the dominant product.
In fact, hybrids currently offer a “best of both worlds” outcome in most cases, particularly when it comes to the high-performance class of cars. This is especially true with electrification still in its infancy, meaning that technology – and most importantly charging infrastructure – still have huge strides to take before we can globally embrace fully electric cars as the convention. Add to this, the research and development of biofuels by some of the biggest players in the industry, and hybrid engines could very well remain a part of the conversation for the years and decades to follow.
Some of the most groundbreaking supercars and hypercars in the world have utilized hybrid technology to impressive effect, all while not neglecting the honest work of reducing emissions. They not only showcase incredible performance credentials (where 0-60 mph in 2.5 s is now the benchmark) but also make a strong case for hybrid technology being as viable (at the very least) for the long haul as it is today.
Here are 10 of the Best Hybrid Engines Ever Produced, curated for your viewing pleasure.
Disclaimer: Our list is likely to include some cars you didn’t realize were actually hybrids. Viewer discretion is advised.
Porsche MR6 V8 Hybrid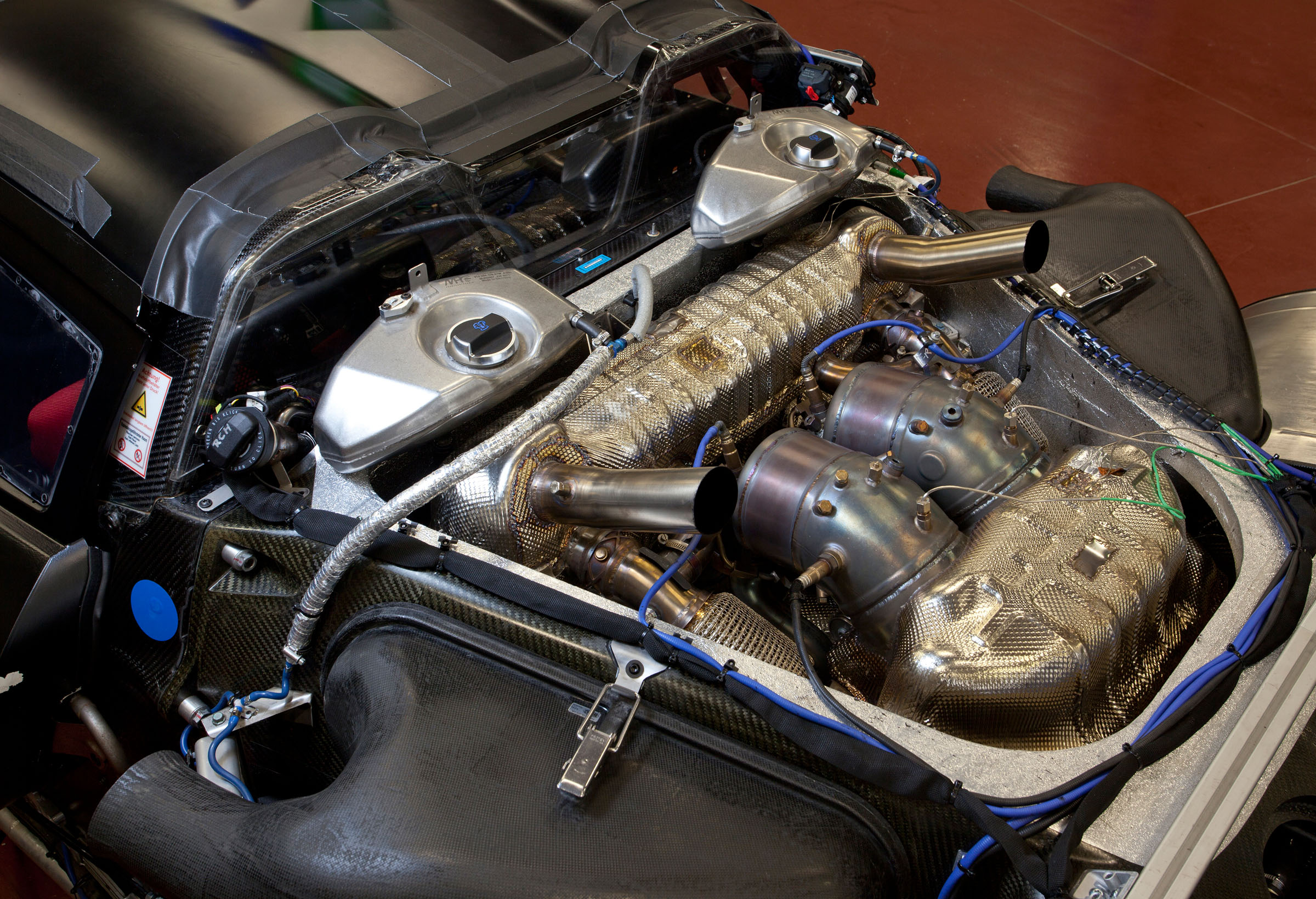
As the spiritual successor to Porsche’s first widely-acknowledged hypercar – the Carrera GT – the 918 Spyder was always going to have to follow its predecessor’s opening act with something quite spectacular of its own. Mission accomplished, I’d say, thanks in huge part to its race-derived MR6 V8 engine. Derivatives of this powerplant were used extensively in ALMS racing competition by the RS Spyder race car, which was designed and built in-house by Porsche in collaboration with Penske Racing. It’s easy to see where the 918 Spyder got its name, but the road-legal car would create its own legacy through the use of a modified drivetrain which increased the engine displacement to 4.6L (from 3.4L in the race versions) and most notably featured a hybrid system with 2 electric motors powered by a 6.8 kWh lithium-ion battery.
The naturally-aspirated combustion unit produced 608 hp by itself while the 2 electric motors – one in the front and one in the rear – provided up to an additional 127 hp and 154 hp to their respective axles. The combined output of the whole system is rated at 887 hp. The 0-62 mph sprint is completed in a blistering 2.2 seconds, with a top speed somewhere north of 211 mph. Being a plug-in hybrid, the 918 Spyder can do all this and run silently in ‘electric-only’ mode for a quoted range of 12 miles. Not exactly an eco-warrior, but hey, at least it provides the framework for its successors to build on.
Ferrari F154FA V8 Hybrid
Ferrari’s F154 family of V8 engines could very well go on to become the G.O.A.T; especially when it has been scrutinized under the incredibly high standards that have been set in the modern era of automobiles. The engine is as potent as it is versatile, powering just about every flavor of Ferrari car since being introduced in 2014; the comfortable California convertible, the grand-touring Roma, the race-bred 488 Pista, and F8 Tributo, and even the 986 hp SF90 Stradale hybrid hypercar.
In the latter form, a 7.9 kWh battery compliments the 4.0L twin-turbocharged V8 and can even bring the SF90 to a speed of 84 mph and complete over 15 miles, all on its own power. By delivering a combined 217 hp via three electric motors, the car is able to produce up to 986 hp with the entire drivetrain on full blast. Aside from a mind-boggling 0-60 mph time of 2.1 seconds, this configuration also makes the SF90 the first mid-engined Ferrari to be all-wheel drive. Handling is also greatly enhanced with torque vectoring now being available on the front axle.
Lamborghini 6.5L naturally-aspirated V12 Hybrid
The Lamborghini Sián is the most notable example of an automobile that uses a supercapacitor – the ‘super’ added because, well, you need a really, really big capacitor to help power a car. In this configuration, the supercapacitor collects and stores energy (primarily from regenerative braking). In certain moments (such as a launch), the supercapacitor dumps all of its energy into an electric motor which immediately and briefly adds an extra 34 hp on top of what the Sián’s 785 hp 6.5L naturally-aspirated V12 engine produces. This means that up to 819 hp is sent to all 4 wheels, with the electric motor integrated into the transmission to reduce weight and improve responsiveness.
As long as the supercapacitor keeps getting recharged – which can be achieved with just seconds of hard braking – there will always be that extra bit of power boost at the car’s beckoning. Compared to an EV battery which takes much, much, longer to fully recharge, and weighs substantially more, you might be wondering why supercapacitors aren’t the dominating technology in electric or hybrid vehicles today. Well, there are a few very important reasons for this. For one, supercapacitors aren’t able to store energy for long periods of time like a battery, making them unviable to be the primary food source for an electric vehicle… at least for now.
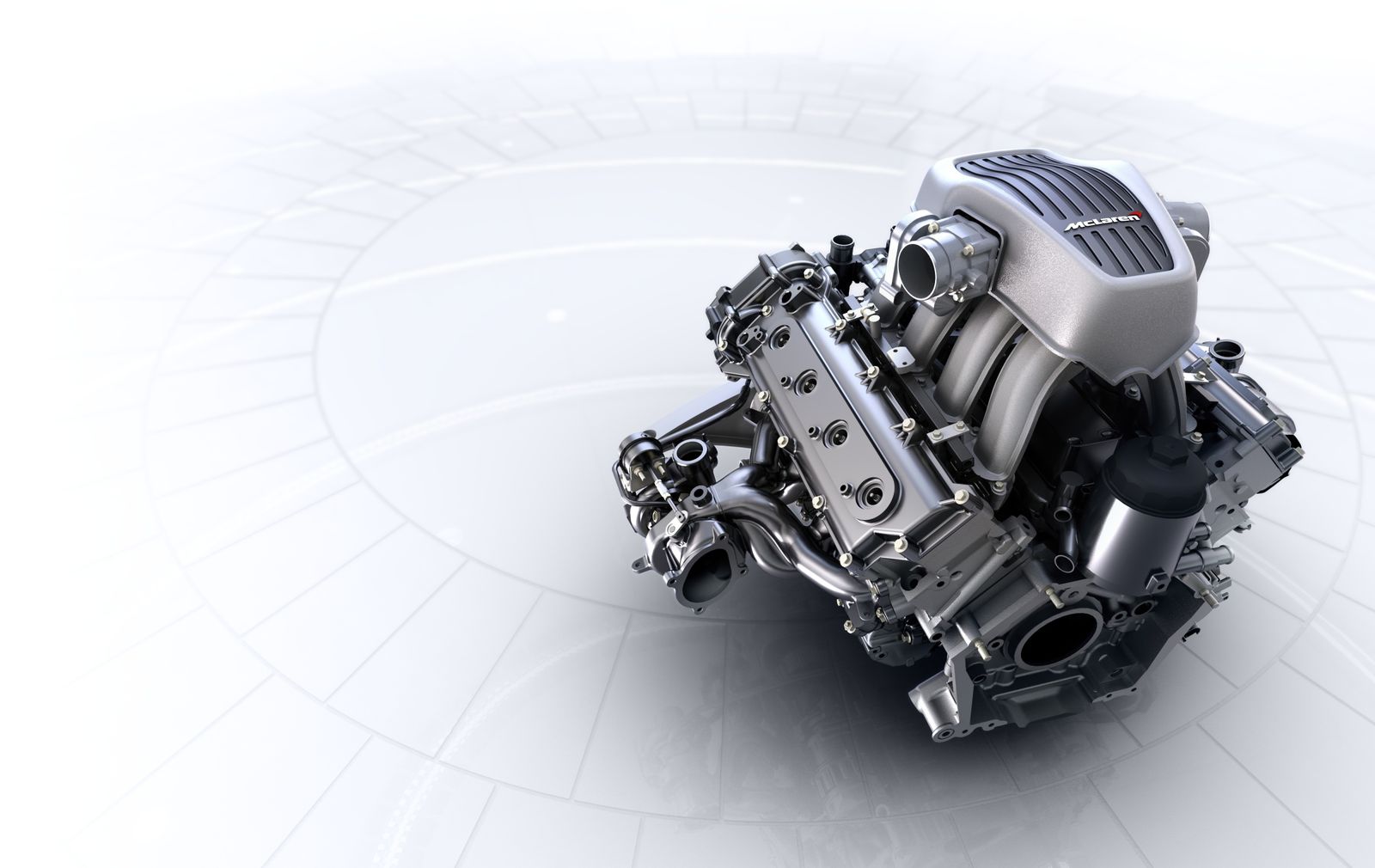
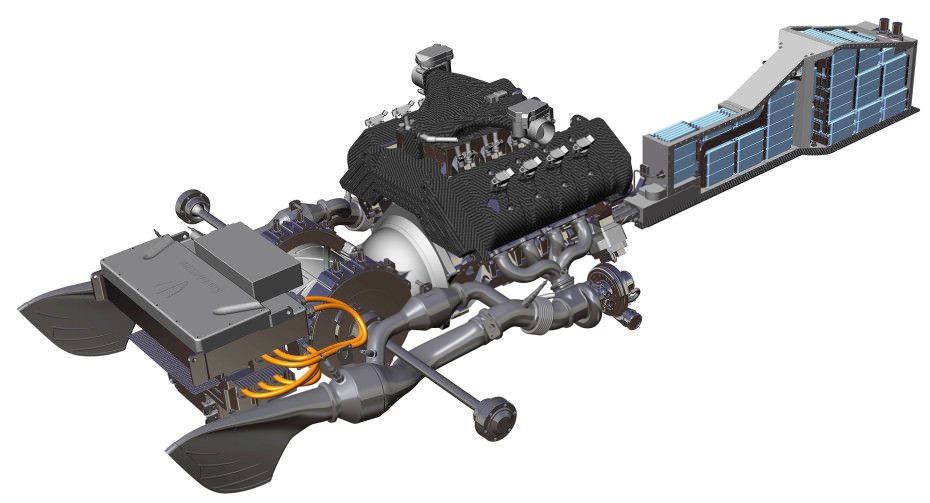
McLaren M840T w/ eMotor
Despite only producing V8-powered automobiles since as recently as 2011 (via the MP4-12C), you could argue that McLaren is now the world’s artisans of the V8 engine, and few would dispute that. After all, it’s virtually all they know these days, with every single McLaren model – bar the V6-hybrid McLaren Artura – fitted with some adaptation of their M838T or M840T twin-turbocharged V8 motors.
The 4.0L M840T features on all of the Super Series cars, which covers the ‘700 range’ of models, plus the addition of the McLaren GT. In its Ultimate form, the 4.0L unit – dubbed the M840TR – produces 814 hp in the McLaren Senna GTR. The McLaren Speedtail hybrid ‘hyper-GT’ produces some 1,035 hp through the combination of an M840T and parallel system eMotor. This setup – in addition to applying the most genius drag-reduction principles in existence today – has allowed the Speedtail to become the fastest production McLaren ever made. Its top speed? 250 mph.
Ferrari F140FE V12 Hybrid
If the F140 had only powered the (2002-2005) Ferrari Enzo – the first Prancing Horse model where it featured – it would have been no less significant or legendary than it is today. The 65-degree V12 engine debuted on the Enzo as a 6.0L naturally-aspirated V12 unit which produced a staggering 651 hp @ 7,800 rpm and 458 lb-ft of torque @ 5,500 rpm. Over the years, 6.3L versions of the F140 have powered the likes of the hybrid LaFerrari and the F12berlinetta. Eventually, the F140 would evolve into what is today, a 6.5L power plant, where it now powers the 812 Competizione.
The Ferrari ‘so nice they named it twice’, also happens to be a hybrid. The Ferrari LaFerrari’s hybrid version of the F140 6.3L V12 power plant produces a total of 950 hp – 788 hp from the naturally-aspirated V12 and 160 hp courtesy of the electric motor, which delivers that power through the differential. This means that 0-60 mph is dispatched in under three seconds, while top speed is rated by Ferrari as somewhere north of 217 mph. Ferrari said that while a side effect of the KERS system – which is tethered to the V12 to continuously recharge itself – was a reduction in emissions, the car would not be capable of running in any type of ‘electric-only’ mode. Ferrari simply was not interested in EVs during the development of the LaFerrari. In fact, the hybrid system’s only function on the halo car was to enhance its performance, and that its relative emissions-friendliness was more of an afterthought than a goal.
BMW B38A15T0 1.5L turbocharged I3 Hybrid
In many ways, the BMW i8 is the least remarkable car on this list. Released during what feels like the olden days now, the 2014 BMW i8 should, however, be credited with revolutionizing the automotive landscape as it pioneered what many consider to be the first high-performance hybrid sports car. Well ahead of its time when it first came out, its powertrain technology was the result of BMW’s visionary approach to a rapidly shifting narrative towards a future focused on sustainability. The eventual overthrowing of the combustion engine would be at the forefront of this movement, with EVs taking their place. The BMW i8 – with its 7.1 kWh lithium-ion battery – would be the earliest creation in this image.
The BMW i8 provides more of a transitional approach to this, rather than a radical one – being a plug-in hybrid as opposed to fully-electric – but would nevertheless be disrupting the status quo. Since its 2014 release, however, the platform fell short of delivering any truly meaningful changes or upgrades until being discontinued in 2020. As time passed, its 369 hp B38A15T0 hybrid engine would appear meager next to emerging hybrid and fully-electric technologies which would go on to make 1,000 hp + figures conceivable in a production road car. But it gave us a hopeful glimpse into the future of automobile electrification, and look where we are now.
The McLaren P1 is considered to be one of three members (the other two being the LaFerrari and 918 Spyder) of the holy hybrid hypercar trinity; the old boy’s club of hypercars, if you will. Like its contemporaries, it fashioned a hybrid drivetrain which allowed it to deliver performance that was once considered unimaginable on a road car. That power comes primarily from a 3.8L twin-turbocharged V8 – the same M838T engine used across the McLaren range but revised to output 727 hp and 531 lb-ft of torque on its own.
Combined with a lightweight and KERS-fed electric motor, that adds a further 176 hp and 192 lb-ft of torque at the driver’s disposal. The 903 hp Ultimate Series model sends all that power to the rear wheels via a 7-speed dual-clutch transmission, allowing it to make the dash from 0-62 mph in just 2.8 seconds. The P1 is also able to hit 186 mph in a mere 16.5 seconds from a standstill, on its way to an electronically-limited top speed of 217 mph. As we learned from Spiderman, “with great power comes great responsibility”; the McLaren P1 exhibits both in abundance, with its plug-in hybrid “twin powerplant” allowing it to run in zero-emissions mode for up to 6.8 miles.
Koenigsegg unveiled its Regera hybrid hypercar model at the 2015 Geneva Motor Show, and since then it has generated plenty of hype amongst car enthusiasts and performance junkies. Besides a regular combustion engine, the Koenigsegg Regera also utilizes 3 electric motors which dole out 700 hp and 663 lb-ft of torque via a 4.5 kWh liquid-cooled battery pack. As a result, the car now produces 1,500 hp (which the company likes to market as 1.11 MW), making it the most powerful hybrid supercar in the world. Its combustion engine is a 5.0L twin-turbocharged V8 that produces an out-of-this-world 1,100 horsepower and 922 lb-ft of torque without electric assistance.
Power is sent to the wheels via Koenigsegg’s new powertrain known as “Koenigsegg Direct Drive”. According to the automaker, “This revolutionary technology removes the traditional gearbox, making the car lighter and more efficient. As the powertrain already produces a combined 1500 hp and with electric propulsion providing instant torque from the Direct Drive system, we did not have to go as extreme on ICE power. Instead, we installed even smaller, faster-spooling turbos on the Regera, further enhancing the car’s drivability and response.” Koenigsegg has gone on to claim that the Regera can theoretically reach top speeds of over 400 km/h, although this has not yet been made official.
Honda/Acura JNC1 3.5L twin-turbocharged V6 Hybrid
The second-generation NSX is the beneficiary of a hybrid drivetrain that produces 573 hp via a twin-turbocharged V6, with 3 electric motors and a 9-speed DCT. It still delivers supercar looks and performance in an everyday livable package. Some pundits call it a “Porsche 918 light” and that says more than anything else about how good the car is. While it is true that the new Acura NSX cannot currently compete with the nostalgia and charm of the car that it replaced, we feel that it is a massively under-appreciated, but worthy supercar. This highly capable vehicle is inostensibly backed by its revolutionary hybrid drivetrain and overall performance figures.
Acura has just announced that they will be producing a limited-edition NSX Type S variant for the 2022 model year. Officially unveiled during Monterrey Car Week, the Type S will be the “quickest, most powerful and best-handling production NSX ever” according to the automaker, with an enhanced version of the 3.5L twin-turbocharged V6 hybrid engine now producing 600 hp and 492 lb-ft of torque. The 9-speed DCT and Super Handling All-Wheel Drive (SH-AWD) have also been optimized to get the most out of the car’s improved performance. While the NSX was never about all-out power, the hybridized powerplant is still good for 0-60 mph in under 3 seconds and a top speed of 191 mph.
Porsche 2.9L, 3.0L V6 E-Hybrid & 4.0L V8 E-Hybrid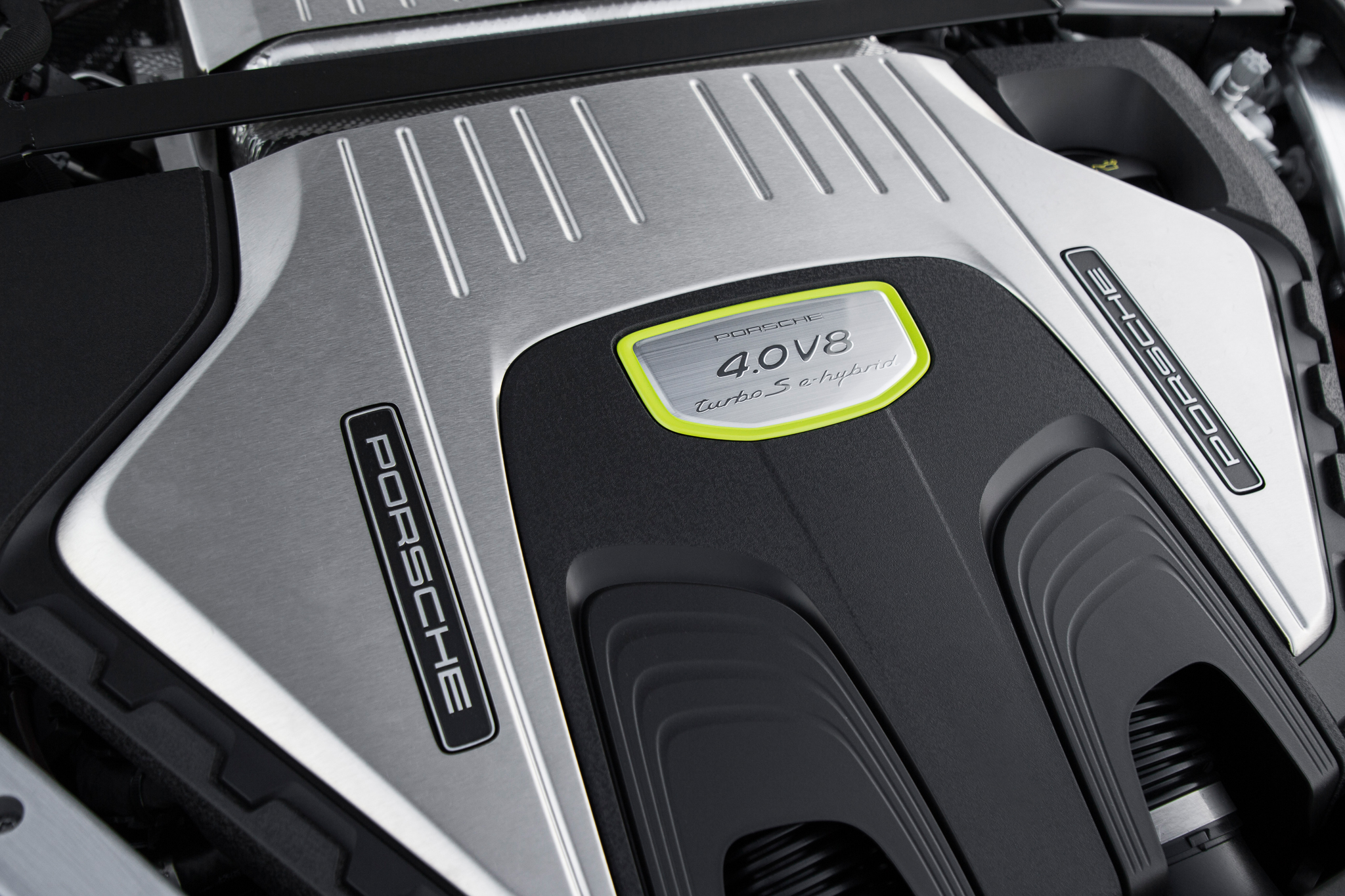
Porsche has provided no shortage of options within any of its model line-ups, with the relatively recent addition of E-Hybrid models serving up even more choices for those seeking a more eco-friendly experience from the brand. While the Taycan is the only model fully committed to electrification, the E-Hybrids are an impressive alternative for those who aren’t quite ready to make the big step over to the other side. Currently, E-Hybrid models can be found within the Panamera and Cayenne model line-ups, and are destined to be in the mix with other models such as the Cayman, 911, and Macan in the not-so-distant future.
The Panamera 4 E-Hybrid is the entry-level E-Hybrid model – at least in size – combining a 2.9L twin-turbocharged V6 which produces 325 hp and 331 lb-ft of torque, with the E-Hybrid electric motor adding up to 134 hp and 295 lb-ft of torque. The lower-priced Cayenne E-Hybrid fashions a hybridized version of the base model’s 3.0L twin-turbocharged V6, while the Cayenne Turbo S E-Hybrid is married to the more robust 4.0L twin-turbocharged V8 which produces a combined 670 hp. The Panamera Turbo S E-Hybrid is at the top of the food chain when it comes to the range, and is the only model (notwithstanding the Cayenne Turbo S E-Hybrid) to feature a hybridized version of the 4.0L twin-turbocharged V8. On its own, the petrol engine produces 563 hp and 567 lb-ft of torque, with the E-Hybrid electric motor adding up to 134 hp and 295 lb-ft of torque.